SUMMARY
Antibodies that block growth hormone signaling by binding the receptor or hormone to stop receptor pairing, based on high-affinity, defined sequences for therapeutic and research use.
The Unmet Need: Effective therapeutic strategies that can precisely and sustainably inhibit growth hormone receptor-mediated signaling
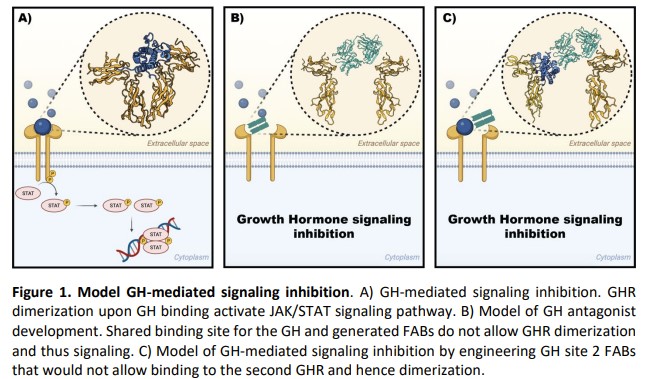
- Growth hormone (GH) plays a central role in regulating growth, metabolism, and tissue repair through its high-affinity receptor on target cells. When GH binds its receptor, sequential engagement of two receptor sites induces dimerization and initiates intracellular signaling cascades that control cell proliferation and metabolic homeostasis. Dysregulated GH signaling underlies disorders such as acromegaly, certain cancers, and metabolic syndromes, creating a pressing need for therapies that selectively and potently disrupt GH–receptor interactions. Effective blockade of this pathway promises to normalize hormone levels, limit aberrant cell growth, and improve quality of life for patients with GH-driven diseases.
-
Current approaches to inhibit GH signaling include somatostatin analogs and GH-receptor antagonists like pegvisomant, but these therapies suffer from incomplete blockade, frequent dosing requirements, and variable patient responses. Somatostatin analogs only partially reduce GH secretion and often cause gastrointestinal side effects. Pegvisomant, while more specific, requires high and repeated injections to maintain effective plasma levels, and some patients develop neutralizing antibodies over time. Additionally, treatment costs remain high and long-term compliance is challenging, highlighting the need for more durable, potent, and patient-friendly GH inhibitors.
The Proposed Solution: Engineered antibodies that inhibit growth hormone signaling by preventing dimerization and receptor recruitment
- The faculty inventor developed a panel of monoclonal antibodies engineered to interrupt growth hormone signaling through two complementary mechanisms. One subset binds directly to the GH receptor’s high-affinity site, sterically blocking hormone engagement and preventing receptor dimerization. A second subset targets the lower-affinity site on GH itself, forming a stable 1:1 antibody–hormone complex that precludes recruitment of a second receptor molecule.
-
These antibodies stand out by offering dual targeting of both receptor and ligand epitopes, providing flexibility in therapeutic strategy and potential to mitigate escape mechanisms. By blocking either receptor dimerization or hormone recruitment, these antibodies not only expand on classical receptor antagonists but also introduce a novel approach to sustained signaling inhibition, backed by detailed sequence information for reproducible synthesis and development.
FIGURE
ADVANTAGES
ADVANTAGES
-
Highly specific inhibition of GH signaling via two complementary antibody mechanisms
-
Ultra-high affinity binding with slow dissociation rates ensures potent and durable inhibition
-
Reproducible synthesis and expression
-
Flexible dosing strategies, including extended inhibition through stable GHR–GH–Fab complexes
APPLICATIONS
- Rare disease- acromegaly
- Oncology
- Research Tools
May 1, 2025
Proof of concept
Patent Pending
Licensing,Co-development
Anthony Kossiakoff