SUMMARY
Engineered recombinant fusion of the dendritic cell growth factor Flt3L to serum albumin to modulate the antigen-presenting compartment and bias it toward tolerance particularly against therapeutic proteins.
The Unmet Need: Novel technologies to modulate the immune system to induce tolerance against therapeutic proteins to improve treatment safety and efficacy.
-
Protein-based therapeutics, including antibody, enzyme replacement, and gene therapies, hold immense promise for treating a wide range of diseases. These biologics offer targeted and effective treatment options. However, a significant challenge lies in their potential to trigger unwanted immune responses in patients.
-
These immune responses, involving both T and B cells, can manifest as hypersensitivity reactions, anaphylaxis, and the development of anti-drug antibodies (ADAs). ADAs, in particular, pose a significant hurdle as they can neutralize the therapeutic protein, leading to reduced efficacy and necessitating dose escalation or treatment discontinuation. Current strategies to mitigate ADA formation, such as dose escalation, are often insufficient, highlighting the urgent need for innovative approaches to induce immune tolerance and enhance the safety and efficacy of these life-changing treatments.
The proposed solution: Novel pathway of Flt3L-mediated immune regulation to attenuate the adaptive reaction to antigenic protein drugs
- The faculty inventor engineered variants of the cytokine Flt3L, known for its role in dendritic cell generation, to induce antigen tolerance and prevent immune responses against therapeutic proteins. The technology employs both native Flt3L and a fusion protein of Flt3L with Serum Albumin (Flt3L-SA) to enhance tolerogenic properties. The Flt3L-SA fusion extends the half-life of Flt3L, leading to a greater accumulation of pro-tolerogenic dendritic cells in lymphoid organs. These engineered constructs promote the differentiation and survival of dendritic cells with a pro-tolerogenic phenotype, enhancing the tolerogenic presentation of antigens to T cells and preventing unwanted immune responses.
-
Notably, this technology demonstrates the ability to induce tolerance without the need for additional immunosuppressants, unlike previous approaches. The technology also highlights the potential of Flt3L-SA in enhancing oral tolerance induction, offering a novel approach to preventing and treating immune-mediated conditions.
FIGURE
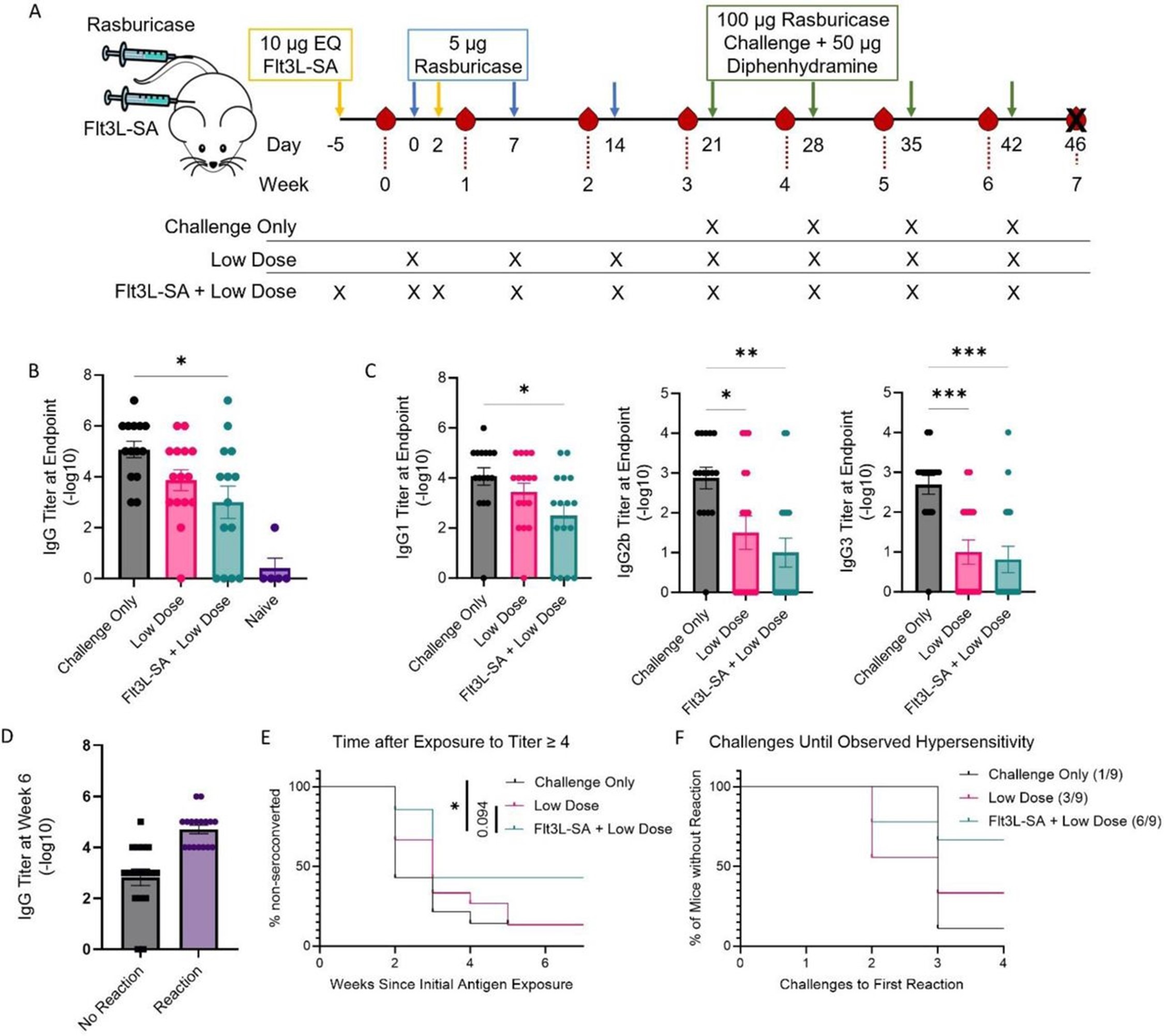
Flt3L-SA treatment in a tolerance induction regimen reduces anti-drug antibody levels and reduces pathogenic reactions to foreign enzymes.
(a) Schematic representing the enzyme replacement challenge model with tolerance induction regimen. Treatments occur on the indicated days, with arrow color representing the treatment. Two induction doses with Flt3L or Flt3L-SA or saline were given with low doses of 5 µg rasburicase, followed by 5 therapeutic doses of 100 µg rasburicase. Flt3L-SA and diphenhydramine are both dosed s.c. and the rasburicase treatments are dosed i.v. Bleeds occur at the indicated weeks with the red drops highlighting the relative timing of the bleeds with respect to treatments. (b) Total rasburicase-specific IgG quantification via titration at experimental endpoint. Significance calculated by one-way ANOVA, significance against naïve not shown. N=5 for naïve group and n= 14-15 for the other three treatments. Error bars represent SEM. (c) Rasburicase-specific IgG subclass titration at experimental endpoint. Significance calculated by one-way ANOVA with n=14-15. Error bars represent SEM. (d) Mice grouped dependent on whether they demonstrated observable reactions at the final challenge against the measured IgG titer preceding the challenge dose. (e) Time until seroconversion to potentially anaphylactic levels of IgG (titer greater than 4) in plasma. Significance calculated via Kaplan-Meier testing. (f) Mice were evaluated 1 hr after each therapeutic challenge infusion for demonstrable anaphylaxis-like symptoms (hunched, ruffled, isolated, and/or cold). Censoring occurred at the first sign of reaction. Numbers indicate mice without demonstrable anti-drug infusion reactions after final challenge over total mice. * for p<0.05, ** for p<0.01, *** for p<0.001.
ADVANTAGES
ADVANTAGES
- Enhances tolerance induction
- Reduces antigen-specific immune responses
- Prevents the formation of anti-drug antibodies
- Promotes accumulation of tolerogenic dendritic cells
- Improves the efficacy and safety of protein-based therapeutics
APPLICATIONS
- Autoimmune disease
- Transplantation
- Off-target drug effects
- Allergy
- Gene therapy enhancement
- Immunomodulation
PUBLICATIONS
-
Engineered Flt3L Drives Tolerogenic State to Attenuate Anti-drug Antibody Responses . Aaron T. Alpar, Rachel P. Wallace, Kirsten C. Refvik, Suzana Gomes, Ani Solanki, Laura T. Gray, Anna J. Slezak, Abigail L. Lauterbach, Lauren A. Hesser, Shijie Cao, J. Emiliano Gómez Medellín, Lauren G. Robinson, Jeffrey A. Hubbell. bioRxiv 2024.03.21.586168; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.03.21.586168
October 16, 2024
Proof of concept
Patent Pending
Licensing,Co-development
Jeffrey Hubbell