SUMMARY
A breakthrough method to systematically select for optimal small guide RNAs using an unbiased approach for improved accuracy and efficiency of all systems of site-directed RNA editing.
The Unmet Need: In vitro assays that reliably predict guide RNA efficiency and specificity before in vivo application
- Over the last two decades, a new area of precision medicine has emerged that utilizes strategically designed oligonucleotides which hybridize to a target RNA and recruit endogenous enzymatic activities for the treatment of disease. For example, synthetic oligonucleotides have been used to modulate RNA splicing (i.e. splice switching) or reduce mRNA expression levels by nucleating RNAi pathways along with a host of other applications.
-
Recently, the recruitment of Adenosine Deaminases that Act on RNAs (ADARs) to direct site-specific editing of RNA has garnered interest as a potential therapeutic modality. ADARs catalyze the conversion of Adenosine (A) to Inosine (I), a biological mimic for Guanosine (G) during translation and other cellular processes. Base recoding by ADARs can be used to correct G-to-A mutations, modulate protein function, or regulate protein splicing and expression when directed to introns within pre-mRNAs or untranslated regions (UTRs) in mature mRNAs.
-
A major challenge confronting the clinical application of site-directed RNA editing (SDRE) is the design of small guide RNAs (gRNAs) that can drive efficient editing. Although many gRNA designs have effectively recruited endogenous ADARs, most of them exceed the size of currently FDA-approved antisense oligos. Additionally, current methods for site-directed RNA editing are often limited by their inefficiency, off-target effects, and the lack of tools for optimizing small guide RNAs (sgRNAs) to improve editing accuracy and specificity.
The proposed solution: Novel selection assay for identifying and optimizing sgRNAs to enhance site-directed RNA editing
- The faculty inventor developed an unbiased in vitro selection assay to identify short gRNAs that promote superior RNA editing of a premature termination codon. The selection assay relies on hairpin substrates in which the target sequence is linked to partially randomized gRNAs in the same molecule, so that gRNA sequences that promote editing can be identified by sequencing.
FIGURE
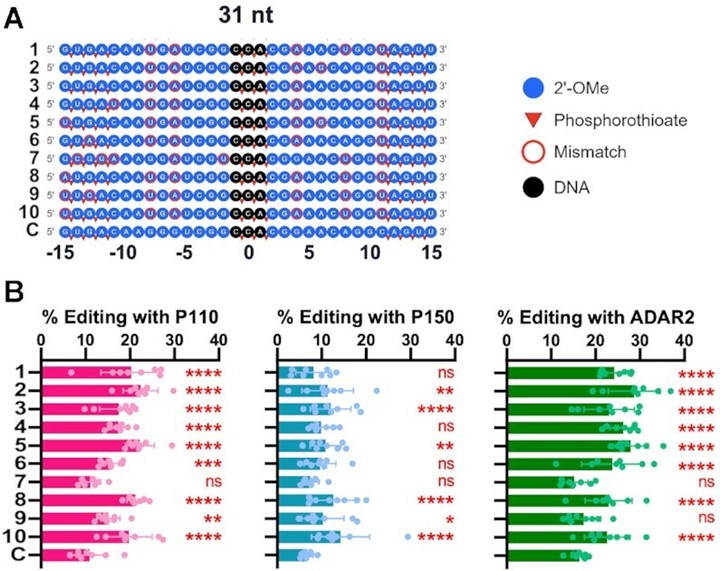
Testing top guide RNAs in cellula. (A) A map of the chemical modifications within the stabilized 31 nt ASOs of the 10 most abundant gRNAs as well as the control gRNA sequences. ASOs (100 nM) were transfected into HEK293T cells transiently expressing mCherry_P2A_eGFP W58X (UAG) and hADAR1-p110, hADAR1-p150 or hADAR2. (B) Percent editing of the top 10 31 nt gRNAs from the selection assay in comparison to the control. Asterisks denote statistically significant differences in comparison to the control gRNA (Two-way ANOVA, **** P < 0.0001, *** P < 0.001, ** P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, n.s. not significant). Error bars represent S.D., and for all data points, n = 8.
ADVANTAGES
ADVANTAGES
- Facilitates the identification of high-performing sgRNAs for RNA editing
- Enhanced specificity, reduced off-target activity
- High-throughput screening of multiple sgRNAs simultaneously
- Reversible edits reducing safety concerns
- Scalability
APPLICATIONS
- Genetic medicine
- Drug development
- Diagnostics
- Agriculture
- Synthetic biology
PUBLICATIONS
- Diaz Quiroz JF, Ojha N, Shayhidin EE, De Silva D, Dabney J, Lancaster A, Coull J, Milstein S, Fraley AW, Brown CR, Rosenthal JJC. Development of a selection assay for small guide RNAs that drive efficient site-directed RNA editing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Apr 24;51(7):e41. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad098. PMID: 36840708; PMCID: PMC10123091
November 26, 2024
Proof of concept
Patent Pending
Licensing,Co-development
Joshua Rosenthal